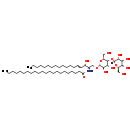| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-10-03 18:21:26 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-04-22 15:45:30 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0011594 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Lactosylceramide (d18:1/22:0) |
|---|
| Description | LacCer(d18:1/22:0), also known as beta-D-Galactosyl-1,4-beta-D-glucosylceramide, is a lactosylceramide (LacCer). Lactosylceramides are members of the class of compounds known as sphingolipids (SPs), or glycosylceramides. SPs are lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases (e.g. sphingosine or sphinganine) that are often covalently bound to a fatty acid derivative through N-acylation. SPs are found in cell membranes, particularly in peripheral nerve cells and the cells found in the central nervous system (including the brain and spinal cord). Sphingolipids are extremely versatile molecules that have functions controlling fundamental cellular processes such as cell division, differentiation, and cell death. Impairments associated with sphingolipid metabolism are associated with many common human diseases such as diabetes, various cancers, microbial infections, diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological syndromes. The biosynthesis and catabolism of sphingolipids involves a large number of intermediate metabolites where many different enzymes are involved. Simple sphingolipids, which include the sphingoid bases and ceramides, make up the early products of the sphingolipid synthetic pathways, while complex sphingolipids may be formed by the addition of head groups to the ceramide template (Wikipedia). LacCers are the most important and abundant of the diosylceramides. LacCers were originally called 'cytolipin H'. They are found in small amounts only in animal tissues, but LacCers have a number of significant biological functions and they are of great importance as biosynthetic precursors to most of the neutral oligoglycosylceramides, sulfatides and gangliosides. In animal tissues, biosynthesis of LacCers involves the addition of a second monosaccharides unit (galactose) as a nucleotide derivative to monoglucosylceramide. This is catalysed by a specific beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase on the lumenal side of the Golgi apparatus. The glucosylceramide precursor must first cross from the cytosolic side of the membrane, possibly via the action of a flippase. The LacCer produced can be further glycosylated or transferred to the plasma membrane. LacCers may assist in stabilizing the plasma membrane and activating receptor molecules in special lipid micro-domains or lipid rafts, as with the cerebrosides. LacCers may also have their own specialized function in the immune system in that LacCers are known to bind to specific bacteria. In addition, it is believed that a number of pro-inflammatory factors activate LacCer synthase to generate LacCer, which in turn activates 'oxygen-sensitive' signalling pathways that affect such cellular processes as proliferation, adhesion, migration and angiogenesis. Dysfunctions in these pathways can lead to several diseases of the cardiovascular system, cancer and other inflammatory conditions, so LacCer metabolism is a potential target for new therapeutic treatments. Beta-D-Galactosyl-1,4-beta-D-glucosylceramide is the second to last step in the synthesis of N-acylsphingosines and is converted. from glucosylceramide via the enzyme beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 6 (EC:2.4.1.-). It can be converted into glucosylceramide via the enzyme beta-galactosidase (EC:3.2.1.23). In terms of its appearance and structure, LacCer(d18:1/22:0) is a colorless solid that consists of an unsaturated 18-carbon sphingoid base with an attached saturated docosanoyl fatty acid side chain. In most mammalian SPs, the 18-carbon sphingoid bases are predominant (PMID: 9759481 ). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| β-LacCer | ChEBI | | CDH | HMDB | | LacCer d18:1/22:0 | HMDB | | LacCer(d18:1/22:0) | HMDB | | Lactosylceramide | HMDB | | Lactosylceramide (d18:1,C22:0) | HMDB | | Lactosylceramide (d18:1/22:0) | HMDB | | Lactosylceramide(d18:1/22:0) | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-4-sphingenine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-D-erythro-sphingosine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-D-sphingosine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-erythro-4-sphingenine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-sphing-4-enine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-sphingenine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-beta-lactosyl-sphingosine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-4-sphingenine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-D-erythro-sphingosine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-D-sphingosine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-erythro-4-sphingenine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-sphing-4-enine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-sphingenine | HMDB | | N-(Docosanoyl)-1-β-lactosyl-sphingosine | HMDB | | N-[(2S,3R,4E)-1-{[4-O-(b-D-galactopyranosyl)-b-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}-3-hydroxyoctadec-4-en-2-yl]docosanamide | HMDB | | N-[(2S,3R,4E)-1-{[4-O-(beta-D-galactopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}-3-hydroxyoctadec-4-en-2-yl]docosanamide | HMDB | | N-[(2S,3R,4E)-1-{[4-O-(β-D-galactopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}-3-hydroxyoctadec-4-en-2-yl]docosanamide | HMDB | | b-D-Galactosyl-(1->4)-b-D-glucosyl-N-(docosanoyl)sphingosine | HMDB | | b-LacCer | HMDB | | b-Lactosyl-N-(docosanoyl)sphingosine | HMDB | | b-Lactosylceramide | HMDB | | beta-D-Galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucosyl-N-(docosanoyl)sphingosine | HMDB | | beta-LacCer | HMDB | | beta-Lactosyl-N-(docosanoyl)sphingosine | HMDB | | beta-Lactosylceramide | HMDB | | β-D-Galactosyl-(1->4)-β-D-glucosyl-N-(docosanoyl)sphingosine | HMDB | | β-Lactosyl-N-(docosanoyl)sphingosine | HMDB | | β-Lactosylceramide | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C52H99NO13 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 946.3414 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 945.711642259 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | N-[(2S,3R,4E)-1-{[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-5-{[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxyoctadec-4-en-2-yl]docosanamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | CDH |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@](CO[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O)(NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@]([H])(O)\C=C\CCCCCCCCCCCCC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C52H99NO13/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-18-19-20-21-22-24-26-28-30-32-34-36-44(57)53-40(41(56)35-33-31-29-27-25-23-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2)39-63-51-49(62)47(60)50(43(38-55)65-51)66-52-48(61)46(59)45(58)42(37-54)64-52/h33,35,40-43,45-52,54-56,58-62H,3-32,34,36-39H2,1-2H3,(H,53,57)/b35-33+/t40-,41+,42+,43+,45-,46-,47+,48+,49+,50+,51+,52-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | QYWVASPEUXEHSY-NNRNTGNWSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as glycosyl-n-acylsphingosines. Glycosyl-N-acylsphingosines are compounds containing a sphingosine linked to a simple glucosyl moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Sphingolipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycosphingolipids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Glycosyl-N-acylsphingosines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Glycosyl-n-acylsphingosine
- Fatty acyl glycoside
- Fatty acyl glycoside of mono- or disaccharide
- Alkyl glycoside
- Disaccharide
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- Fatty amide
- N-acyl-amine
- Oxane
- Fatty acyl
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxamide group
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Oxacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Acetal
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organooxygen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | - beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1)-N-acylsphingosine (CHEBI:62109 )
|
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | - Cell membrane
- Endosome
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00or-0111004809-3d472fd9629198430f93 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0gb9-0222116912-c8f59a495e4350a4c0cc | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03dj-1774914752-d7bcdacf6bb987f798e6 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-002f-0312004419-e066b9667abc0b46f46f | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03fr-3504043903-eef9aa9b4e5171faba55 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0059-4902111200-70ea0c13127e2b5893e5 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0feb-2500018905-a33e29571335a1877ac8 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0uxs-3900013301-bdf42a957cb2cb56277c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-01vx-4910021100-8244f0288c2d525ca600 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-0101000109-77350ecf3f81c1ee5cb5 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-06r6-7593003234-65c1a3db4ccd6c3d034e | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-06z9-3219020000-0d5f3fd1908f635e3896 | View in MoNA |
|---|
|
|---|