| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-10-03 18:34:05 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-04-22 15:49:01 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0012203 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Cis-zeatin-O-glucoside |
|---|
| Description | Cis-zeatin-O-glucoside, also known as O-beta-D-glucosylzeatin, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as fatty acyl glycosides of mono- and disaccharides. Fatty acyl glycosides of mono- and disaccharides are compounds composed of a mono- or disaccharide moiety linked to one hydroxyl group of a fatty alcohol or of a phosphorylated alcohol (phosphoprenols), a hydroxy fatty acid or to one carboxyl group of a fatty acid (ester linkage) or to an amino alcohol. Cis-zeatin-O-glucoside is a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). |
|---|
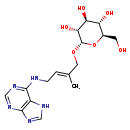
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-cis-zeatin | HMDB | | O-beta-D-Glucosylzeatin | HMDB | | O-beta-delta-Glucopyranosyl-cis-zeatin | HMDB | | O-beta-delta-Glucosylzeatin | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C16H23N5O6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 381.3837 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 381.164833493 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-{[(2E)-2-methyl-4-[(7H-purin-6-yl)amino]but-2-en-1-yl]oxy}oxane-3,4,5-triol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-{[(2E)-2-methyl-4-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-yl]oxy}oxane-3,4,5-triol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | C\C(CO[C@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O)=C/CNC1=NC=NC2=C1NC=N2 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C16H23N5O6/c1-8(2-3-17-14-10-15(19-6-18-10)21-7-20-14)5-26-16-13(25)12(24)11(23)9(4-22)27-16/h2,6-7,9,11-13,16,22-25H,3-5H2,1H3,(H2,17,18,19,20,21)/b8-2+/t9-,11-,12+,13-,16+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | UUPDCCPAOMDMPT-GIHYWFGSSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as fatty acyl glycosides of mono- and disaccharides. Fatty acyl glycosides of mono- and disaccharides are compounds composed of a mono- or disaccharide moiety linked to one hydroxyl group of a fatty alcohol or of a phosphorylated alcohol (phosphoprenols), a hydroxy fatty acid or to one carboxyl group of a fatty acid (ester linkage) or to an amino alcohol. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl glycosides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Fatty acyl glycosides of mono- and disaccharides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Fatty acyl glycoside of mono- or disaccharide
- Alkyl glycoside
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- 6-alkylaminopurine
- 6-aminopurine
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Secondary aliphatic/aromatic amine
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Pyrimidine
- Imidolactam
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Imidazole
- Secondary alcohol
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Secondary amine
- Polyol
- Acetal
- Azacycle
- Oxacycle
- Primary alcohol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | |
|---|