| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 22:30:37 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-06-04 20:45:48 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0000430 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D |
|---|
| Description | 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D, also known as vitamin D or 24-hydroxycalcidiol, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as vitamin d and derivatives. Vitamin D and derivatives are compounds containing a secosteroid backbone, usually secoergostane or secocholestane. 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D is possibly soluble (in water) and an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). |
|---|
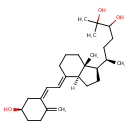
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (3b,5Z,7E)-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-3,24,25-triol | HMDB | | 24,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol | HMDB | | 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin | HMDB | | 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 | HMDB | | 24-Hydroxycalcidiol | HMDB | | Vitamin D | HMDB | | 24,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D3 | HMDB | | (24R)-24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 | HMDB | | 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3, (3beta,5Z,7E,24R)-isomer | HMDB | | 24,25 Dihydroxycholecalciferol | HMDB | | Dihydroxyvitamin D3, 24,25 | HMDB | | 24R,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol | HMDB | | 24,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 | HMDB | | 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 | HMDB | | 24,25-Dihydroxy-vitamin D | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C27H44O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 416.6365 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 416.329045274 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (6R)-6-[(1R,3aS,4E,7aR)-4-{2-[(1Z,5R)-5-hydroxy-2-methylidenecyclohexylidene]ethylidene}-7a-methyl-octahydro-1H-inden-1-yl]-2-methylheptane-2,3-diol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 40013-87-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[C@H](CCC(O)C(C)(C)O)[C@H]1CC[C@@]2([H])\C(CCC[C@]12C)=C\C=C1\C[C@H](O)CCC1=C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C27H44O3/c1-18-8-12-22(28)17-21(18)11-10-20-7-6-16-27(5)23(13-14-24(20)27)19(2)9-15-25(29)26(3,4)30/h10-11,19,22-25,28-30H,1,6-9,12-17H2,2-5H3/b20-10+,21-11-/t19-,22-,23-,24+,25?,27-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | FCKJYANJHNLEEP-OIMXRAFZSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as vitamin d and derivatives. Vitamin D and derivatives are compounds containing a secosteroid backbone, usually secoergostane or secocholestane. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Vitamin D and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Vitamin D and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Triterpenoid
- Tertiary alcohol
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | - Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4i-7029200000-c84dd427774a8bd55bf4 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-014i-1312049000-f6115b14a152464f5e1b | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_3_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00l2-0119200000-7bcd78fea8093a8230ae | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a5a-2369100000-04f3fb5d7d655a9ce470 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0zgi-4389100000-269c6b355710e7dcd9b8 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-0004900000-7bbe3ea5eae60b2a2059 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-05mk-0009300000-4137913e2e1e7271894c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0079-9006000000-b2d6915fde38c349870a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00lr-0439300000-d0f3435842264a17a15a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00rx-4579100000-2ffe9e7393dd492716a0 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0avi-2960000000-4329739a1dba4656972b | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014j-0007900000-764d7cf399a810ff092c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0671-3109300000-5c39962acfb73b3f737d | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-01ri-2129300000-7f78982c59e2cf08742c | View in MoNA |
|---|
|
|---|
| General References | - Reeve LE, Jorgensen NA, DeLuca HF: Vitamin D compounds in cows' milk. J Nutr. 1982 Apr;112(4):667-72. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.4.667. [PubMed:6279806 ]
- Hollis BW, Roos BA, Draper HH, Lambert PW: Vitamin D and its metabolites in human and bovine milk. J Nutr. 1981 Jul;111(7):1240-8. doi: 10.1093/jn/111.7.1240. [PubMed:6788913 ]
- Park, Y. W; Juárez, Manuela ; Ramos, M.; Haenlein, G. F. W. (2007). Park, Y. W; Juárez, Manuela ; Ramos, M.; Haenlein, G. F. W.. Physico-chemical characteristics of goat and sheep milk. Small Ruminant Res.(2007) 68:88-113 doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2006.09.013. Small Ruminant Research.
|
|---|