| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 23:05:18 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-05-21 16:28:28 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0003556 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Chitobiose |
|---|
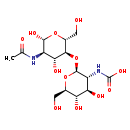
| Description | Chitobiose, also known as CBS or chitobiose, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. Chitobiose is possibly soluble (in water) and an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Chitobiose can be converted into N-acetyl-D-glucosamine; which is mediated by the enzyme Beta-hexosaminidase subunit alpha. In cattle, chitobiose is involved in the metabolic pathway called the amino sugar metabolism pathway. Chitobiose is a potentially toxic compound. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| CBS | HMDB | | Chitodextrin | HMDB | | Diacetylchitobiose | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H26N2O12 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 426.3731 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 426.148574306 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | [(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-5-acetamido-4,6-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]carbamic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-5-acetamido-4,6-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-ylcarbamic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 577-76-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(=O)N[C@H]1[C@H](O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2NC(O)=O)[C@@H]1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H26N2O12/c1-4(20)16-7-11(23)12(6(3-19)27-13(7)24)29-14-8(17-15(25)26)10(22)9(21)5(2-18)28-14/h5-14,17-19,21-24H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,16,20)(H,25,26)/t5-,6-,7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-,13-,14+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | HSRZMOSQMYFZBL-CGKOVJDHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Acylaminosugars |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Acylaminosugar
- N-acyl-alpha-hexosamine
- Disaccharide
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- Oxane
- Acetamide
- Carbamic acid
- Carbamic acid derivative
- Carboxamide group
- Hemiacetal
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Secondary alcohol
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Acetal
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Alcohol
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0pvj-8639200000-6c3347b5dbe3b3f9c2c3 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004i-4431129000-6a66b04ba8ecc3e96ae2 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0kyr-1029500000-cd23e338ffeece93c8d2 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0l6r-1596200000-dfb00a2cbc9b167897ce | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03xu-8879000000-3e843b304076403ca7ad | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0f6x-2291000000-09b27f575d21cfe14882 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0pi0-7595200000-da369f627875da3f63d6 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-114i-9720000000-64ac9bbabb821260cc03 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00b9-0019200000-24a05e9c2b0aef9d97c2 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0acc-4229100000-ea4966254c54c4e1c671 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-054o-9342000000-d67950a3955201982141 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a6r-0140900000-421220daa6be82144fb9 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-1984300000-1dd32aad758490afc646 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0wmu-9710000000-b4b4aee4a3748673917c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
|
|---|