| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 22:20:35 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-05-20 23:10:21 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0000181 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
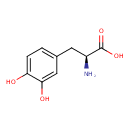
| Common Name | L-Dopa |
|---|
| Description | L-Dopa, also known as l-dopa or l-dopa, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tyrosine and derivatives. Tyrosine and derivatives are compounds containing tyrosine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of tyrosine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. L-Dopa is a drug which is used for the treatment of idiopathic parkinson's disease (paralysis agitans), postencephalitic parkinsonism, symptomatic parkinsonism which may follow injury to the nervous system by carbon monoxide intoxication, and manganese intoxication. L-Dopa exists as a solid, possibly soluble (in water), and a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa) molecule. L-Dopa exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. L-Dopa participates in a number of enzymatic reactions, within cattle. In particular, L-Dopa and tetrahydrobiopterin can be converted into dopamine and 4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin through the action of the enzyme aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase. In addition, L-Dopa can be converted into dopaquinone through its interaction with the enzyme tyrosinase. In cattle, L-dopa is involved in the metabolic pathway called the tyrosine metabolism pathway. L-Dopa is a potentially toxic compound. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (-)-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | ChEBI | | (-)-Dopa | ChEBI | | 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine | ChEBI | | 3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE | ChEBI | | 3-Hydroxy-L-tyrosine | ChEBI | | beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | ChEBI | | beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | ChEBI | | Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine | ChEBI | | Dopar | ChEBI | | L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | ChEBI | | Levodopa | ChEBI | | Levodopum | ChEBI | | b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | Generator | | Β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | Generator | | b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | Β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | L-b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | L-Β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine | Generator | | (2S)-2-Amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate | HMDB | | (2S)-2-Amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid | HMDB | | 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine | HMDB | | 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine | HMDB | | b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-a-L-alanine | HMDB | | Bendopa | HMDB | | beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-L-alanine | HMDB | | Cidandopa | HMDB | | Dihydroxyphenylalanine | HMDB | | Dopaflex | HMDB | | Dopaidan | HMDB | | Dopal | HMDB | | Dopalina | HMDB | | Doparkine | HMDB | | Doparl | HMDB | | Dopasol | HMDB | | Dopaston | HMDB | | Dopastone | HMDB | | Dopastral | HMDB | | Dopicar | HMDB | | Doprin | HMDB | | Eldopal | HMDB | | Eldopar | HMDB | | Eldopatec | HMDB | | Eurodopa | HMDB | | Helfo-dopa | HMDB | | Insulamina | HMDB | | L-(-)-Dopa | HMDB | | L-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alanine | HMDB | | L-4-5-Dihydroxyphenylalanine | HMDB | | L-b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-a-alanine | HMDB | | L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-alanine | HMDB | | L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine | HMDB | | Laradopa | HMDB | | Larodopa | HMDB | | Ledopa | HMDB | | Levedopa | HMDB | | Levopa | HMDB | | Maipedopa | HMDB | | Parda | HMDB | | Pardopa | HMDB | | Prodopa | HMDB | | Syndopa | HMDB | | Veldopa | HMDB | | Weldopa | HMDB | | 3 Hydroxy L tyrosine | HMDB | | Roche brand OF levodopa | HMDB | | L 3,4 Dihydroxyphenylalanine | HMDB | | L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine | HMDB | | Medphano brand OF levodopa | HMDB | | L Dopa | HMDB | | Roberts brand OF levodopa | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C9H11NO4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 197.1879 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 197.068807845 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | levodopa |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 59-92-7 |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@@H](CC1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C9H11NO4/c10-6(9(13)14)3-5-1-2-7(11)8(12)4-5/h1-2,4,6,11-12H,3,10H2,(H,13,14)/t6-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIESA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tyrosine and derivatives. Tyrosine and derivatives are compounds containing tyrosine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of tyrosine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tyrosine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tyrosine or derivatives
- Phenylalanine or derivatives
- 3-phenylpropanoic-acid
- Alpha-amino acid
- Amphetamine or derivatives
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Catechol
- 1-hydroxy-4-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Aralkylamine
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Detected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 285 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 5.0 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | -2.39 | SANGSTER (1993) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (4 TMS) | splash10-014i-0790000000-b2f7f063a2c8197c7edd | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0690000000-622497b3104c6082a45d | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (4 TMS) | splash10-00xr-9350000000-b0cc4636931d2de64d81 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (4 TMS) | splash10-014i-0590000000-4474e81e4226bb4e1d4c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0790000000-b2f7f063a2c8197c7edd | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0690000000-622497b3104c6082a45d | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00xr-9350000000-b0cc4636931d2de64d81 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0590000000-4474e81e4226bb4e1d4c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-1890000000-646d209fa1943582a336 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0690000000-720ed87e98a0d9f1721d | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0fk9-3900000000-266d9baeda773fe1fb22 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0002-4193000000-8c76bf85d8a897e9403c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_2_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_3_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-0uea-0900000000-8eb71aa0cc8622f097a2 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-0a59-2900000000-bf63b9b719959b82b543 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-056r-9300000000-a78b0b31dd33fe8479a7 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0f6t-0911000000-15affa616923dfb9c45a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-22d8267801d0eb0b73c2 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-001i-0900000000-2c310034a1a871502b4c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0udi-0900000000-5e6020c952f741531fcb | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0007-0970100000-49594dae82ce73e734e6 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-001i-0900000000-2183a68f58b951f3f1c7 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-03di-0900000000-0030db588fbd92c5b761 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0006-0090000000-544615463a975baae9e4 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0002-0729111000-0a20b01f58fff8ad7ef0 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-c8095a31ed4b3dbbc646 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-03di-0190000000-41515cba3a6929721859 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0002-0900000000-8074c509ef5bae1129fc | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0006-0502193020-497bfad7ba247159ca00 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-0b0d4b6dcb7f1fa24e1a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-004i-0029800000-05f40324c8c1fec7963a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0006-0000090000-c0cd80185ce47b30e5fe | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive | splash10-0002-0900000000-df116b84981cf4a1371a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) 30V, Positive | splash10-0f6t-0900000000-1c1c39a8880442ea18df | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udj-0900000000-cf54b26df05181b0d2fc | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0900000000-d506f2673b114b8e38d2 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00di-8900000000-1699873cb7650f62b5bc | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0002-0900000000-a0d81bfc4868b0d1cbf9 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
|
|---|