| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 22:33:19 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-06-04 20:36:49 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0000595 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydrogen carbonate |
|---|
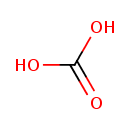
| Description | Hydrogen carbonate, also known as H2CO3 or [co(OH)2], belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic carbonic acids. Organic carbonic acids are compounds comprising the carbonic acid functional group. Hydrogen carbonate exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to plants to humans. Hydrogen carbonate, with regard to humans, has been found to be associated with several diseases such as bartter syndrome, type 2, antenatal, renal tubular acidosis, distal, rta type 1, and monocarboxylate transporter 1 deficiency; hydrogen carbonate has also been linked to several inborn metabolic disorders including 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coa lyase deficiency and hawkinsinuria. Based on a literature review a significant number of articles have been published on Hydrogen carbonate. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| [CO(OH)2] | ChEBI | | Dihydrogen carbonate | ChEBI | | H2CO3 | ChEBI | | Koehlensaeure | ChEBI | | Dihydrogen carbonic acid | Generator | | Hydrogen carbonic acid | Generator | | Carbonate | Generator, HMDB | | Acid OF air | HMDB | | Aerial acid | HMDB | | Bisodium carbonate | HMDB | | Calcined | HMDB | | Carbonic acid sodium salt | HMDB | | Consal | HMDB | | Crystol carbonate | HMDB | | Disodium carbonate | HMDB | | Mild alkali | HMDB | | Na-X | HMDB | | Oxyper | HMDB | | Sal soda | HMDB | | Salt OF soda | HMDB | | Scotch soda | HMDB | | Soda | HMDB | | Soda ash | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate anhydrous | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate hydrated | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate | HMDB | | Solvay soda | HMDB | | Trona soda ash | HMDB | | Tronalight light soda ash | HMDB | | Acid, carbonic | MeSH, HMDB | | Carbonic acid | MeSH, HMDB | | Ions, bicarbonate | MeSH | | Carbonate, hydrogen | MeSH | | Carbonates, hydrogen | MeSH | | Bicarbonate ion | MeSH | | Hydrogen carbonates | MeSH | | Bicarbonates | MeSH | | Bicarbonate ions | MeSH | | Carbonic acid ions | MeSH | | Ions, carbonic acid | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | CH2O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 62.0248 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 62.00039393 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | carbonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | carbonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 463-79-6 |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/CH2O3/c2-1(3)4/h(H2,2,3,4) |
|---|
| InChI Key | BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic carbonic acids. Organic carbonic acids are compounds comprising the carbonic acid functional group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Organic carbonic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Organic carbonic acids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Organic carbonic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Carbonic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-310dbbc64fba7d9c667e | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00du-9300000000-b9ab1da5629a3dfff55f | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-53429210d3161a8e792f | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-65bbb10c2768f3746b62 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-b6afca3e3ac002546879 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-0ef3797aeb5276c64c90 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-5b50453541e6f14e35be | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-5b50453541e6f14e35be | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-3142be69389832d3eb4b | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-3142be69389832d3eb4b | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-3142be69389832d3eb4b | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-65a6c4ac46a60ccd0a02 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-75ba60e3edf4ccfcfbe0 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-a1e091bb1f5fa6e9cbc7 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
|
|---|