| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 23:01:52 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-05-11 20:56:01 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0002865 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Oxytocin |
|---|
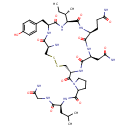
| Description | Oxytocin, also known as (arg8)-vasotocin or alpha-hypophamine, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as oligopeptides. These are organic compounds containing a sequence of between three and ten alpha-amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Oxytocin is a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (Arg8)-vasopressin | HMDB | | (Arg8)-vasotocin | HMDB | | alpha-Hypophamine | HMDB | | Argipressin | HMDB | | Argpressin acetate | HMDB | | Biotinyl-(arg8)-vasopressin | HMDB | | Cys-tyr-ile-GLN-asn-cys-pro-arg-gly-NH2 | HMDB | | Cys-tyr-ile-GLN-asn-cys-pro-leu-gly-NH2 | HMDB | | Cys-tyr-ile-THR-asn-cys-gly-leu-gly-NH2 | HMDB | | Cys-tyr-phe-GLN-asn-cys-pro-arg-gly-NH2 | HMDB | | Cys-tyr-phe-GLN-asn-cys-pro-lys-gly-NH2 | HMDB | | Disulfide bridge cys1-cys6 | HMDB | | Gly-leu-pro-c | HMDB | | Ocytocin | HMDB | | OXT | HMDB | | Oxytocin 10 usp units in dextrose 5% | HMDB | | Oxytocin 20 usp units in dextrose 5% | HMDB | | Oxytocin 5 usp units in dextrose 5% | HMDB | | Oxytocin acetate | HMDB | | Oxytocin injection | HMDB | | Pitocin | HMDB | | Syntocinon | HMDB | | (2S)-2-[({1-[(4R,7S,10S,13S,16S,19R)-19-amino-13-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-6,9,12,15,18-pentahydroxy-10-[2-(C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)ethyl]-7-[(C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)methyl]-16-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentaazacycloicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaene-4-carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)methylidene)amino]-N-[(C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)methyl]-4-methylpentanimidate | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C43H66N12O12S2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 1007.187 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 1006.436457016 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-({1-[(4R,7S,10S,13S,16S,19R)-19-amino-13-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-10-(2-carbamoylethyl)-7-(carbamoylmethyl)-16-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentaazacycloicosane-4-carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}formamido)-N-(carbamoylmethyl)-4-methylpentanamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2S)-2-({1-[(4R,7S,10S,13S,16S,19R)-19-amino-13-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-10-(2-carbamoylethyl)-7-(carbamoylmethyl)-16-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentaazacycloicosane-4-carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}formamido)-N-(carbamoylmethyl)-4-methylpentanamide |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 50-56-6 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC[C@H](C)[C@@H]1NC(=O)[C@H](CC2=CC=C(O)C=C2)NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CSSC[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CC(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(N)=O)NC1=O)C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)NCC(N)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C43H66N12O12S2/c1-5-22(4)35-42(66)49-26(12-13-32(45)57)38(62)51-29(17-33(46)58)39(63)53-30(20-69-68-19-25(44)36(60)50-28(40(64)54-35)16-23-8-10-24(56)11-9-23)43(67)55-14-6-7-31(55)41(65)52-27(15-21(2)3)37(61)48-18-34(47)59/h8-11,21-22,25-31,35,56H,5-7,12-20,44H2,1-4H3,(H2,45,57)(H2,46,58)(H2,47,59)(H,48,61)(H,49,66)(H,50,60)(H,51,62)(H,52,65)(H,53,63)(H,54,64)/t22-,25-,26-,27-,28-,29-,30-,31?,35-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | XNOPRXBHLZRZKH-MQYCRUOZSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as oligopeptides. These are organic compounds containing a sequence of between three and ten alpha-amino acids joined by peptide bonds. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Oligopeptides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-oligopeptide
- Cyclic alpha peptide
- Leucine or derivatives
- Proline or derivatives
- Macrolactam
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid amide
- N-substituted-alpha-amino acid
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- N-acylpyrrolidine
- Pyrrolidine carboxylic acid or derivatives
- Pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Fatty amide
- N-acyl-amine
- Fatty acyl
- Benzenoid
- Pyrrolidine
- Tertiary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Organic disulfide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Primary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxamide group
- Lactam
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Primary amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-01w0-7211090007-02ded9f4fb62188bcd1c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-9100000102-9932076684dd100467c1 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00di-9842101200-f6f6d97cad6b1952b979 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00dr-9012104006-d088f89ac80bb947ef8c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0kj6-3011011009-145137bb0cf8acc97408 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-001l-6970111341-f07368f08e3e4bb508d5 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000002-0e271ec3ffcffeb3ba00 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4u-9001000015-43fe697177f713ba1dde | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9500024454-88f21ec58b7e9cd96f8a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000002-f636a43bb80aae6d594f | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4l-4000000239-156bd2db8a73e819195e | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9100002101-0b1da7f1f7e4c461135f | View in MoNA |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
|
|---|