Showing metabocard for Guanine (BMDB0000132)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 22:19:59 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2020-06-04 20:46:51 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMDB ID | BMDB0000132 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Guanine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Guanine, also known as G or mearlmaid aa, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purines and purine derivatives. These are aromatic heterocyclic compounds containing a purine moiety, which is formed a pyrimidine-ring ring fused to an imidazole ring. Guanine exists as a solid, possibly soluble (in water), and a moderately basic compound (based on its pKa) molecule. Guanine exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Guanine has been found to be associated with several diseases known as colorectal cancer, alzheimer's disease, lewy body disease, and frontotemporal dementia; also guanine has been linked to the inborn metabolic disorders including lesch-nyhan syndrome. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
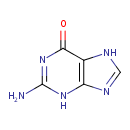
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C5H5N5O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 151.1261 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 151.049409807 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 2-amino-6,7-dihydro-3H-purin-6-one | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 2-aminohypoxanthine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 73-40-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | NC1=NC(=O)C2=C(N1)N=CN2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H5N5O/c6-5-9-3-2(4(11)10-5)7-1-8-3/h1H,(H4,6,7,8,9,10,11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purines and purine derivatives. These are aromatic heterocyclic compounds containing a purine moiety, which is formed a pyrimidine-ring ring fused to an imidazole ring. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Imidazopyrimidines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Purines and purine derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Purines and purine derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofunction | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Application | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biospecimen Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000132 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB02377 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB004222 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001501 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 744 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Compound ID | C00242 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | GUANINE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | 34363 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Guanine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | 315 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound | 764 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 16235 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Xiao, Xuhua; Ma, Weiyong. One-pot synthesis of guanine. Faming Zhuanli Shenqing Gongkai Shuomingshu (2007), 10pp. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Nucleotide transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes a salvage reaction resulting in the formation of AMP, that is energically less costly than de novo synthesis.
- Gene Name:
- APRT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q56JW4
- Molecular weight:
- 19537.0
Reactions
| Guanosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate → Guanine + Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate | details |
- General function:
- Nucleotide transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Converts guanine to guanosine monophosphate, and hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate. Transfers the 5-phosphoribosyl group from 5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate onto the purine. Plays a central role in the generation of purine nucleotides through the purine salvage pathway (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HPRT1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3SZ18
- Molecular weight:
- 24498.0
Reactions
| Guanosine monophosphate + Pyrophosphate → Guanine + Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate | details |
- General function:
- Nucleotide transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- The purine nucleoside phosphorylases catalyze the phosphorolytic breakdown of the N-glycosidic bond in the beta-(deoxy)ribonucleoside molecules, with the formation of the corresponding free purine bases and pentose-1-phosphate.
- Gene Name:
- PNP
- Uniprot ID:
- P55859
- Molecular weight:
- 32037.0
Reactions
| Guanosine + Hydrogen phosphate → Guanine + Ribose 1-phosphate | details |
| Deoxyguanosine + Hydrogen phosphate → Guanine + Deoxyribose 1-phosphate | details |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl binding
- Specific function:
- Functions as signal transducer for the rod photoreceptor RHO (PubMed:21285355, PubMed:23303210, PubMed:28655769, PubMed:8259210). Required for normal RHO-mediated light perception by the retina (By similarity). Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), such as the photoreceptor RHO. The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and alternates between an active, GTP-bound state and an inactive, GDP-bound state (PubMed:21285355, PubMed:28655769, PubMed:8259210, PubMed:8208289, PubMed:7969474). Activated RHO promotes GDP release and GTP binding (PubMed:21285355, PubMed:28655769). Signaling is mediated via downstream effector proteins, such as cGMP-phosphodiesterase (PubMed:21285355).
- Gene Name:
- GNAT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P04695
- Molecular weight:
- 39966.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) alpha subunit playing a prominent role in bitter and sweet taste transduction as well as in umami (monosodium glutamate, monopotassium glutamate, and inosine monophosphate) taste transduction.
- Gene Name:
- GNAT3
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C7Q4
- Molecular weight:
- 40332.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNG11
- Uniprot ID:
- Q5E9F0
- Molecular weight:
- 8594.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. Transducin is an amplifier and one of the transducers of a visual impulse that performs the coupling between rhodopsin and cGMP-phosphodiesterase.
- Gene Name:
- GNAT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P04696
- Molecular weight:
- 40144.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- GTPase that associates with pre-60S ribosomal subunits in the nucleolus and is required for their nuclear export and maturation.
- Gene Name:
- GNL2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q2YDL0
- Molecular weight:
- 83469.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. Acts as an activator of phospholipase C. Transduces FFAR4 signaling in response to long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs).
- Gene Name:
- GNA11
- Uniprot ID:
- P38409
- Molecular weight:
- 42070.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GNAI3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3ZCA7
- Molecular weight:
- 40536.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTPase activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P11017
- Molecular weight:
- 37331.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems.
- Gene Name:
- GNA14
- Uniprot ID:
- P38408
- Molecular weight:
- 41499.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNG12
- Uniprot ID:
- Q28024
- Molecular weight:
- 8057.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers in numerous signaling pathways controlled by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Signaling involves the activation of adenylyl cyclases, resulting in increased levels of the signaling molecule cAMP (PubMed:2022671, PubMed:9395396, PubMed:11087399, PubMed:15591060, PubMed:16766715, PubMed:19243146). GNAS functions downstream of several GPCRs, including beta-adrenergic receptors. Stimulates the Ras signaling pathway via RAPGEF2 (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GNAS
- Uniprot ID:
- P04896
- Molecular weight:
- 45709.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in numerous signaling cascades. The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and alternates between an active, GTP-bound state and an inactive, GDP-bound state. Signaling by an activated GPCR promotes GDP release and GTP binding. The alpha subunit has a low GTPase activity that converts bound GTP to GDP, thereby terminating the signal. Both GDP release and GTP hydrolysis are modulated by numerous regulatory proteins (By similarity). Signaling is mediated via effector proteins, such as adenylate cyclase. Inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, leading to decreased intracellular cAMP levels (By similarity). The inactive GDP-bound form prevents the association of RGS14 with centrosomes and is required for the translocation of RGS14 from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. Required for normal cytokinesis during mitosis (By similarity). Required for cortical dynein-dynactin complex recruitment during metaphase (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GNAI1
- Uniprot ID:
- P63097
- Molecular weight:
- 40361.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Gnas
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6U8D6
- Molecular weight:
- 23994.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNG3
- Uniprot ID:
- P63214
- Molecular weight:
- 8305.0
- General function:
- Involved in activation of phospholipase C activity by G
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GNB1
- Uniprot ID:
- A7E3V7
- Molecular weight:
- 37030.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Stabilizes TERF1 telomeric association by preventing TERF1 recruitment by PML. Stabilizes TERF1 protein by preventing its ubiquitination and hence proteasomal degradation. Does so by interfering with TERF1-binding to FBXO4 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Required for cell proliferation. By stabilizing TRF1 protein during mitosis, promotes metaphase-to-anaphase transition. Stabilizes MDM2 protein by preventing its ubiquitination, and hence proteasomal degradation. By acting on MDM2, may affect TP53 activity. Required for normal processing of ribosomal pre-rRNA. Binds GTP (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GNL3L
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3T0J9
- Molecular weight:
- 64837.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNGT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P02698
- Molecular weight:
- 8544.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. The G(o) protein function is not clear. Stimulated by RGS14 (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GNAO1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08239
- Molecular weight:
- 40067.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNGT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P50154
- Molecular weight:
- 7728.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNG5
- Uniprot ID:
- P63217
- Molecular weight:
- 7318.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P63212
- Molecular weight:
- 7850.0
- General function:
- Not Available
- Specific function:
- Subunit of both mTORC1 and mTORC2, which regulates cell growth and survival in response to nutrient and hormonal signals. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino acids. Growth factor-stimulated mTORC1 activation involves a AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of TSC1-TSC2, which leads to the activation of the RHEB GTPase that potently activates the protein kinase activity of mTORC1. Amino acid-signaling to mTORC1 requires its relocalization to the lysosomes mediated by the Ragulator complex and the Rag GTPases. Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. mTORC1 phosphorylates EIF4EBP1 and releases it from inhibiting the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates S6K1 at 'Thr-389', which then promotes protein synthesis by phosphorylating PDCD4 and targeting it for degradation. Within mTORC1, LST8 interacts directly with MTOR and enhances its kinase activity. In nutrient-poor conditions, stabilizes the MTOR-RPTOR interaction and favors RPTOR-mediated inhibition of MTOR activity. mTORC2 is also activated by growth factors, but seems to be nutrient-insensitive. mTORC2 seems to function upstream of Rho GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton, probably by activating one or more Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors. mTORC2 promotes the serum-induced formation of stress-fibers or F-actin. mTORC2 plays a critical role in AKT1 'Ser-473' phosphorylation, which may facilitate the phosphorylation of the activation loop of AKT1 on 'Thr-308' by PDK1 which is a prerequisite for full activation. mTORC2 regulates the phosphorylation of SGK1 at 'Ser-422'. mTORC2 also modulates the phosphorylation of PRKCA on 'Ser-657' (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- MLST8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q17QU5
- Molecular weight:
- 35920.0
- General function:
- Involved in guanyl nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q4JM29
- Molecular weight:
- 11661.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction.
- Gene Name:
- GNB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P62871
- Molecular weight:
- 37377.0
- General function:
- Involved in GTP binding
- Specific function:
- GTPase that associates with pre-60S ribosomal subunits in the nucleolus and is required for their nuclear export and maturation.
- Gene Name:
- GNL2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q1JP69
- Molecular weight:
- 83483.0
- General function:
- Involved in signal transducer activity
- Specific function:
- Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction. Plays a role in the regulation of adenylyl cyclase signaling in certain regions of the brain. Plays a role in the formation or stabilzation of a G protein heterotrimer (G(olf) subunit alpha-beta-gamma-7) that is required for adenylyl cyclase activity in the striatum (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GNG7
- Uniprot ID:
- P30671
- Molecular weight:
- 7552.0