| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-10-03 17:57:54 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-05-11 19:49:31 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0010055 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | PIP2(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) |
|---|
| Description | PIP2(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphates. These are phosphatidylinositol bisphosphates in which the two phosphate groups are at C-4 and C-5 of the inositol moiety. PIP2(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). |
|---|
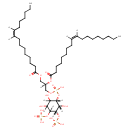
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| {[(1S,2S,3S)-3-({[(2R)-3-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(phosphonooxy)cyclohexyl]oxy}phosphonate | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C43H81O19P3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 995.023 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 994.458491382 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(1S,2S,3S)-3-({[(2R)-3-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(phosphonooxy)cyclohexyl]oxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | [(1S,2S,3S)-3-{[(2R)-3-[(9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyloxy]-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(phosphonooxy)cyclohexyl]oxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | [H]\C(CCCCCC)=C(/[H])CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@]([H])(COP(O)(=O)O[C@@]1([H])C([H])(O)C([H])(O)C([H])(OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@]([H])(OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@]1([H])O)OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C([H])=C(\[H])CCCCCCCC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C43H81O19P3/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-18-20-22-24-26-28-30-32-37(45)59-35(33-57-36(44)31-29-27-25-23-21-19-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2)34-58-65(55,56)62-41-38(46)39(47)42(60-63(49,50)51)43(40(41)48)61-64(52,53)54/h14,16-18,35,38-43,46-48H,3-13,15,19-34H2,1-2H3,(H,55,56)(H2,49,50,51)(H2,52,53,54)/b16-14-,18-17-/t35-,38?,39?,40+,41+,42?,43+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | RDFHKVSRQVTPND-ASZSQGGESA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphates. These are phosphatidylinositol bisphosphates in which the two phosphate groups are at C-4 and C-5 of the inositol moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Glycerophospholipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycerophosphoinositol phosphates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Diacylglycerophosphoinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
- Diacylglycerophosphoinositol
- Glycerophosphoinositol
- Inositol phosphate
- Dialkyl phosphate
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Fatty acid ester
- Cyclohexanol
- Fatty acyl
- Alkyl phosphate
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Cyclitol or derivatives
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Polyol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | - Cell membrane
- Intracellular membrane
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | |
|---|