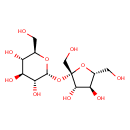
Showing metabocard for Sucrose (BMDB0000258)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 22:27:32 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2020-06-04 22:55:57 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMDB ID | BMDB0000258 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Sucrose | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Sucrose, also known as cane sugar or saccharose, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as o-glycosyl compounds. These are glycoside in which a sugar group is bonded through one carbon to another group via a O-glycosidic bond. Sucrose exists as a solid, possibly soluble (in water), and an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa) molecule. Sucrose exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C12H22O11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 342.2965 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 342.116211546 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | sucrose | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 57-50-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(O[C@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C12H22O11/c13-1-4-6(16)8(18)9(19)11(21-4)23-12(3-15)10(20)7(17)5(2-14)22-12/h4-11,13-20H,1-3H2/t4-,5-,6-,7-,8+,9-,10+,11-,12+/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as o-glycosyl compounds. These are glycoside in which a sugar group is bonded through one carbon to another group via a O-glycosidic bond. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | O-glycosyl compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected but not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofunction | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Application | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biospecimen Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000258 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB02772 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB003715 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001151 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Compound ID | C00089 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | SUCROSE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Sucrose | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound | 5988 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 17992 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Fitremann, Juliette; Queneau, Yves; Maitre, Jean-Paul; Bouchu, Alain. Co-melting of solid sucrose and multivalent cation soaps for solvent-free synthesis of sucrose esters. Tetrahedron Letters (2007), 48(23), 4111-4114. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Only showing the first 50 proteins. There are 91 proteins in total.
Enzymes
- General function:
- Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the initial reaction in O-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis, the transfer of an N-acetyl-D-galactosamine residue to a serine or threonine residue on the protein receptor. May participate in synthesis of oncofetal fibronectin. Has activity toward Muc1a, Muc2, EA2 and fibronectin peptides (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GALNT6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q5EA41
- Molecular weight:
- 71138.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the initial reaction in O-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis, the transfer of an N-acetyl-D-galactosamine residue to a serine or threonine residue on the protein receptor. Has a broad spectrum of substrates for peptides such as EA2, Muc5AC, Muc1a, Muc1b and Muc7.
- Gene Name:
- GALNT1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07537
- Molecular weight:
- 64192.0
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Multifunctional protein that plays a central role in the cellular response to oxidative stress. The two major activities of APEX1 are DNA repair and redox regulation of transcriptional factors. Functions as a apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endodeoxyribonuclease in the DNA base excision repair (BER) pathway of DNA lesions induced by oxidative and alkylating agents. Initiates repair of AP sites in DNA by catalyzing hydrolytic incision of the phosphodiester backbone immediately adjacent to the damage, generating a single-strand break with 5'-deoxyribose phosphate and 3'-hydroxyl ends. Does also incise at AP sites in the DNA strand of DNA/RNA hybrids, single-stranded DNA regions of R-loop structures, and single-stranded RNA molecules. Has a 3'-5' exoribonuclease activity on mismatched deoxyribonucleotides at the 3' termini of nicked or gapped DNA molecules during short-patch BER. Possesses a DNA 3' phosphodiesterase activity capable of removing lesions (such as phosphoglycolate) blocking the 3' side of DNA strand breaks. May also play a role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression by participating in DNA demethylation. Acts as a loading factor for POLB onto non-incised AP sites in DNA and stimulates the 5'-terminal deoxyribose 5'-phosphate (dRp) excision activity of POLB. Plays a role in the protection from granzymes-mediated cellular repair leading to cell death. Also involved in the DNA cleavage step of class switch recombination (CSR). On the other hand, APEX1 also exerts reversible nuclear redox activity to regulate DNA binding affinity and transcriptional activity of transcriptional factors by controlling the redox status of their DNA-binding domain, such as the FOS/JUN AP-1 complex after exposure to IR. Involved in calcium-dependent down-regulation of parathyroid hormone (PTH) expression by binding to negative calcium response elements (nCaREs). Together with HNRNPL or the dimer XRCC5/XRCC6, associates with nCaRE, acting as an activator of transcriptional repression. Stimulates the YBX1-mediated MDR1 promoter activity, when acetylated at Lys-6 and Lys-7, leading to drug resistance. Acts also as an endoribonuclease involved in the control of single-stranded RNA metabolism. Plays a role in regulating MYC mRNA turnover by preferentially cleaving in between UA and CA dinucleotides of the MYC coding region determinant (CRD). In association with NMD1, plays a role in the rRNA quality control process during cell cycle progression. Associates, together with YBX1, on the MDR1 promoter. Together with NPM1, associates with rRNA. Binds DNA and RNA (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- APEX1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23196
- Molecular weight:
- 35570.0
- General function:
- Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GALNT6
- Uniprot ID:
- A6H6Z5
- Molecular weight:
- 71152.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GALNT13
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08DM9
- Molecular weight:
- 64063.0
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Bifunctional DNA N-glycosylase with associated apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) lyase function that catalyzes the first step in base excision repair (BER), the primary repair pathway for the repair of oxidative DNA damage. The DNA N-glycosylase activity releases the damaged DNA base from DNA by cleaving the N-glycosidic bond, leaving an AP site. The AP lyase activity cleaves the phosphodiester bond 3' to the AP site by a beta-elimination. Primarily recognizes and repairs oxidative base damage of pyrimidines.
- Gene Name:
- NTHL1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q2KID2
- Molecular weight:
- 33645.0
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Essential for the degradation of glycogen in lysosomes (PubMed:10723725). Has highest activity on alpha-1,4-linked glycosidic linkages, but can also hydrolyze alpha-1,6-linked glucans.
- Gene Name:
- GAA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9MYM4
- Molecular weight:
- 104757.0
Reactions
| Sucrose + Water → D-Galactose + D-Fructose | details |
| Alpha-D-Glucose + D-Fructose → Sucrose + Water | details |
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- MASP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08DW4
- Molecular weight:
- 81268.0
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Involved in base excision repair of DNA damaged by oxidation or by mutagenic agents. Has DNA glycosylase activity towards 5-hydroxyuracil and other oxidized derivatives of cytosine with a preference for mismatched double-stranded DNA (DNA bubbles). Has low or no DNA glycosylase activity towards thymine glycol, 2-hydroxyadenine, hypoxanthine and 8-oxoguanine. Has AP (apurinic/apyrimidinic) lyase activity and introduces nicks in the DNA strand. Cleaves the DNA backbone by beta-delta elimination to generate a single-strand break at the site of the removed base with both 3'- and 5'-phosphates (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- NEIL2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6IE77
- Molecular weight:
- 36392.0
- General function:
- Involved in 3'-5' exonuclease activity
- Specific function:
- Nuclease involved in single-strand and double-strand DNA break repair. Recruited to sites of DNA damage through interaction with poly(ADP-ribose), a polymeric post-translational modification synthesized transiently at sites of chromosomal damage to accelerate DNA strand break repair reactions. Displays apurinic-apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease and 3'-5' exonuclease activities in vitro. Also able to introduce nicks at hydroxyuracil and other types of pyrimidine base damage. Together with PARP3, promotes the retention of the LIG4-XRCC4 complex on chromatin and accelerate DNA ligation during non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ).
- Gene Name:
- APLF
- Uniprot ID:
- A0JNH9
- Molecular weight:
- 54326.0
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Receptor for secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2). Also able to bind to snake PA2-like toxins. Although its precise function remains unclear, binding of sPLA2 to its receptor participates in both positive and negative regulation of sPLA2 functions as well as clearance of sPLA2. Binding of sPLA2-IB/PLA2G1B induces various effects depending on the cell type, such as activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade to induce cell proliferation, the production of lipid mediators, selective release of arachidonic acid in bone marrow-derived mast cells. In neutrophils, binding of sPLA2-IB/PLA2G1B can activate p38 MAPK to stimulate elastase release and cell adhesion. May be involved in responses in proinflammatory cytokine productions during endotoxic shock. Also has endocytic properties and rapidly internalizes sPLA2 ligands, which is particularly important for the clearance of extracellular sPLA2s to protect their potent enzymatic activities. The soluble secretory phospholipase A2 receptor form is circulating and acts as a negative regulator of sPLA2 functions by blocking the biological functions of sPLA2-IB/PLA2G1B and sPLA2-X/PLA2G10.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2R1
- Uniprot ID:
- P49259
- Molecular weight:
- 168651.0
- General function:
- Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Controls the flux of glucose into the hexosamine pathway. Most likely involved in regulating the availability of precursors for N- and O-linked glycosylation of proteins (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GFPT2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q08DQ2
- Molecular weight:
- 77081.0
- General function:
- Replication, recombination and repair
- Specific function:
- Functions as a weak apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endodeoxyribonuclease in the DNA base excision repair (BER) pathway of DNA lesions induced by oxidative and alkylating agents. Initiates repair of AP sites in DNA by catalyzing hydrolytic incision of the phosphodiester backbone immediately adjacent to the damage, generating a single-strand break with 5'-deoxyribose phosphate and 3'-hydroxyl ends. Displays also double-stranded DNA 3'-5' exonuclease, 3'-phosphodiesterase activities. Shows robust 3'-5' exonuclease activity on 3'-recessed heteroduplex DNA and is able to remove mismatched nucleotides preferentially. Shows fairly strong 3'-phosphodiesterase activity involved in the removal of 3'-damaged termini formed in DNA by oxidative agents. In the nucleus functions in the PCNA-dependent BER pathway. Required for somatic hypermutation (SHM) and DNA cleavage step of class switch recombination (CSR) of immunoglobulin genes. Required for proper cell cycle progression during proliferation of peripheral lymphocytes (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- APEX2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q5E9N9
- Molecular weight:
- 56938.0
- General function:
- Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
- Specific function:
- Scavenger receptor that displays several functions associated with host defense. Promotes binding and phagocytosis of Gram-positive, Gram-negative bacteria and yeast. Mediates the recognition, internalization and degradation of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein (oxLDL) by vascular endothelial cells. Binds to several carbohydrates including Gal-type ligands, D-galactose, L- and D-fucose, GalNAc, T and Tn antigens in a calcium-dependent manner and internalizes specifically GalNAc in nurse-like cells. Binds also to sialyl Lewis X or a trisaccharide and asialo-orosomucoid (ASOR) (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- COLEC12
- Uniprot ID:
- A6QP79
- Molecular weight:
- 81751.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Galectin that binds lactose and a related range of sugars. May be involved in the assembly of adherens junctions (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- LGALS4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3T0D6
- Molecular weight:
- 37171.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- MBL-A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q5I2B0
- Molecular weight:
- 26308.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GALNT16
- Uniprot ID:
- A6QLD9
- Molecular weight:
- 62727.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GALNT4
- Uniprot ID:
- A7YY74
- Molecular weight:
- 66549.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GALNT12
- Uniprot ID:
- A6QLX6
- Molecular weight:
- 66725.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GALNTL4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q0IIK7
- Molecular weight:
- 69508.0
- General function:
- Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- LGALS3
- Uniprot ID:
- A6QLZ0
- Molecular weight:
- 27646.0
- General function:
- Involved in cation binding
- Specific function:
- Carbohydrate-binding lectin with a preference for chitin. Has no chitinase activity. May play a role in tissue remodeling and in the capacity of cells to respond to and cope with changes in their environment. Plays a role in T-helper cell type 2 (Th2) inflammatory response and IL-13-induced inflammation, regulating allergen sensitization, inflammatory cell apoptosis, dendritic cell accumulation and M2 macrophage differentiation. Facilitates invasion of pathogenic enteric bacteria into colonic mucosa and lymphoid organs. Mediates activation of AKT1 signaling pathway and subsequent IL8 production in colonic epithelial cells. Regulates antibacterial responses in lung by contributing to macrophage bacterial killing, controlling bacterial dissemination and augmenting host tolerance. Also regulates hyperoxia-induced injury, inflammation and epithelial apoptosis in lung (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- CHI3L1
- Uniprot ID:
- P30922
- Molecular weight:
- 43032.0
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- SLC35A2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8SPM1
- Molecular weight:
- 41437.0
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- SELPLG
- Uniprot ID:
- A7WPA6
- Molecular weight:
- 45236.0
- General function:
- Involved in G-protein coupled receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and neuron guidance via its interactions with FLRT2 and FLRT3 that are expressed at the surface of adjacent cells. Plays a role in the development of glutamatergic synapses in the cortex. Important in determining the connectivity rates between the principal neurons in the cortex.
- Gene Name:
- ADGRL3
- Uniprot ID:
- O97827
- Molecular weight:
- 176051.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- In presence of calcium ions, it binds to surfactant phospholipids and contributes to lower the surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the alveoli of the mammalian lung and is essential for normal respiration. Enhances the expression of MYO18A/SP-R210 on alveolar macrophages.
- Gene Name:
- SFTPA1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6RXL1
- Molecular weight:
- 26381.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Binds high-mannose carbohydrates in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner (By similarity). Functional receptor for alpha-mannans on C.albicans hypheas. Plays an important role in the host defense against C.albicans infection by inducing TH17 cell differentiation. Recognizes also, in a mannose-dependent manner, allergens from house dust mite and fungi, by promoting cysteinyl leukotriene production. Recognizes soluble elements from the eggs of Shistosoma mansoni altering adaptive immune responses. Transduces signals through an Fc receptor gamma chain /FCER1G and Syk-CARD9-NF-kappa-B-dependent pathway (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- CLEC6A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3LUH2
- Molecular weight:
- 23738.0
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- KLRJ1
- Uniprot ID:
- A6QPD3
- Molecular weight:
- 31350.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- REG4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3ZCG9
- Molecular weight:
- 18401.0
- General function:
- Involved in G-protein coupled receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- O97806
- Molecular weight:
- 152642.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Calcium-binding chaperone that promotes folding, oligomeric assembly and quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via the calreticulin/calnexin cycle. This lectin interacts transiently with almost all of the monoglucosylated glycoproteins that are synthesized in the ER. Interacts with the DNA-binding domain of NR3C1 and mediates its nuclear export. Involved in maternal gene expression regulation. May participate in oocyte maturation via the regulation of calcium homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- CALR
- Uniprot ID:
- P52193
- Molecular weight:
- 48039.0
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- KLRJ1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q863I0
- Molecular weight:
- 31336.0
- General function:
- Involved in MHC class I protein binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- KLRC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q95JG6
- Molecular weight:
- 9429.0
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- APCS
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3T004
- Molecular weight:
- 25183.0
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Plays a role as a receptor for the recognition of MHC class I HLA-E molecules by NK cells and some cytotoxic T-cells.
- Gene Name:
- KLRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q863H3
- Molecular weight:
- 21927.0
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Insulin-regulated facilitative glucose transporter, which plays a key role in removal of glucose from circulation. Response to insulin is regulated by its intracellular localization: in the absence of insulin, it is efficiently retained intracellularly within storage compartments in muscle and fat cells. Upon insulin stimulation, translocates from these compartments to the cell surface where it transports glucose from the extracellular milieu into the cell.
- Gene Name:
- SLC2A4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q27994
- Molecular weight:
- 55084.0
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Cell-surface glycoprotein having a role in immunoadhesion. Mediates in the adhesion of blood neutrophils in cytokine-activated endothelium through interaction with SELPLG/PSGL1. May have a role in capillary morphogenesis.
- Gene Name:
- SELE
- Uniprot ID:
- P98107
- Molecular weight:
- 53200.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q56JW0
- Molecular weight:
- 17784.0
- General function:
- Involved in receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Cell surface receptor that protects target cells against natural killer cell-mediated lysis. Modulates signaling cascades and mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of target MAP kinases (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- CLEC12B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q2NL33
- Molecular weight:
- 31835.0
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide-sugar transmembrane transporter
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- SLC35A5
- Uniprot ID:
- A6QPI1
- Molecular weight:
- 48142.0
- General function:
- Involved in G-protein coupled receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- O97804
- Molecular weight:
- 152741.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- LGALS8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q2YDD7
- Molecular weight:
- 40127.0
- General function:
- Involved in protein binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q32SI4
- Molecular weight:
- 45383.0
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Facilitative glucose transporter, which is responsible for constitutive or basal glucose uptake. Has a very broad substrate specificity; can transport a wide range of aldoses including both pentoses and hexoses. Most important energy carrier of the brain: present at the blood-brain barrier and assures the energy-independent, facilitative transport of glucose into the brain.
- Gene Name:
- SLC2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P27674
- Molecular weight:
- 54132.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Receptor that mediates the recognition, internalization and degradation of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein (oxLDL) by vascular endothelial cells. OxLDL is a marker of atherosclerosis that induces vascular endothelial cell activation and dysfunction, resulting in pro-inflammatory responses, pro-oxidative conditions and apoptosis. Its association with oxLDL induces the activation of NF-kappa-B through an increased production of intracellular reactive oxygen and a variety of pro-atherogenic cellular responses including a reduction of nitric oxide (NO) release, monocyte adhesion and apoptosis. In addition to binding oxLDL, it acts as a receptor for the HSP70 protein involved in antigen cross-presentation to naive T-cells in dendritic cells, thereby participating in cell-mediated antigen cross-presentation. Also involved in inflammatory process, by acting as a leukocyte-adhesion molecule at the vascular interface in endotoxin-induced inflammation. Also acts as a receptor for advanced glycation end (AGE) products, activated platelets, monocytes, apoptotic cells and both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
- Gene Name:
- OLR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P79391
- Molecular weight:
- 30892.0
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Insulin-regulated facilitative hexose transporter that mediates the transport of glucose and fructose. Also able to mediate the transport of dehydroascorbate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC2A8
- Uniprot ID:
- P58354
- Molecular weight:
- 51417.0
- General function:
- Involved in sugar binding
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- LGALS2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q0VBW6
- Molecular weight:
- 13487.0
- General function:
- Involved in G-protein coupled receptor activity
- Specific function:
- Calcium-independent receptor of low affinity for alpha-latrotoxin, an excitatory neurotoxin present in black widow spider venom which triggers massive exocytosis from neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Receptor probably implicated in the regulation of exocytosis.
- Gene Name:
- ADGRL2
- Uniprot ID:
- O97817
- Molecular weight:
- 165547.0
- General function:
- Involved in protein homodimerization activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ASGR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q32KM0
- Molecular weight:
- 32369.0
- General function:
- Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- CL43
- Uniprot ID:
- B7FEK7
- Molecular weight:
- 33616.0
Only showing the first 50 proteins. There are 91 proteins in total.