| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 23:03:28 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-05-21 16:26:51 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0003288 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Selenocysteine |
|---|
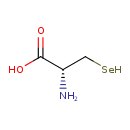
| Description | Selenocysteine, also known as Selenocysteine, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. Selenocysteine is possibly soluble (in water) and a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). Selenocysteine exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Selenocysteine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions, within cattle. In particular, Selenocysteine can be converted into L-alanine and hydrogen selenide; which is mediated by the enzyme selenocysteine lyase. In addition, Selenocysteine and 2-ketobutyric acid can be biosynthesized from selenocystathionine; which is mediated by the enzyme cystathionine gamma-lyase. In cattle, selenocysteine is involved in the metabolic pathway called the selenoamino acid metabolism pathway. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3-Selenyl-L-alanine | ChEBI | | L-Selenocystein | ChEBI | | L-Selenozystein | ChEBI | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-selanylpropanoate | HMDB | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-selanylpropanoic acid | HMDB | | 3-Seleno-alanine | HMDB | | 3-Selenoalanine | HMDB | | L-Selenocysteine | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H7NO2Se |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 168.05 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 168.964200301 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-2-amino-3-selanylpropanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | L-selenocysteine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 3614-08-2 |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@@H](C[SeH])C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2Se/c4-2(1-7)3(5)6/h2,7H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZKZBPNGNEQAJSX-REOHCLBHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | L-alpha-amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - L-alpha-amino acid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Amine
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Selenol
- Primary amine
- Organoselenium compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-5900000000-827b47dc191649f521ac | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-5900000000-32e999fe6e3d67e322cb | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-01b9-0900000000-fadd5a69b2b225d034ac | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01b9-0900000000-8fe6412cebc1ca99fe59 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00dl-5900000000-2408222e037ff9db752a | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-0900000000-91ba91d891f89ff1fc23 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00kk-6900000000-67c579b8ba30e155bcb3 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00di-9200000000-0b58b77f13cec3df121d | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-0900000000-59cfe0ab1984ab09d7af | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-01b9-7900000000-6f634fdb5ee7a8437ca7 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-014i-1900000000-0f58b4784272be073705 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-01b9-0900000000-3a288e1fc4c42cfb333c | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05fr-0900000000-c29c42f6924485632ad3 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-2900000000-8f03b287aede9d710058 | View in MoNA |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | View in JSpectraViewer |
|---|
|
|---|